- 9-1-1
- 1.
- abstract data type
- see interface
- adjacency list
- 12.2
- adjacency matrix
- 12.1
- algorithmic complexity attack
- 5.4
- amortized cost
- 1.5.0.0.1
- amortized running time
- 1.5
- ancestor
- 6.
- array
- circular
- 2.3
-
- 2.4
-
- 2.3
- arrays
- 2.
-
- 2.1
- asymptotic notation
- 1.3.3
- AVL tree
- 9.4
 -tree
-tree
- 14.3
 -tree
-tree
- 14.3
 -tree
-tree
- 14.2
- backing array
- 2.
-
- 1.8
-
- 3.3
- Bibliography on Hashing
- 5.4
- big-Oh notation
- 1.3.3
- binary heap
- 10.
- binary logarithm
- 1.3.1
- binary search
- 13.2
| 14.2.1
- binary search tree
- 6.2
- height balanced
- 9.4
- partial rebuilding
- 8.
- random
- 7.1
- randomized
- 7.3
- red-black
- 9.
- size-balanced
- 6.3
- versus skiplist
- 4.5
- binary search tree property
- 6.2
- binary tree
- 6.
- complete
- 10.1
- heap-ordered
- 10.1
- search
- 6.2
- binary-tree traversal
- 6.1.2
-
- 10.1
-

- 6.2
-
- 6.1
-
- 13.1
- binomial coefficients
- 1.3.2
- binomial heap
- 10.3
- black node
- 9.2
- black-height property
- 9.2
- block
- 14.
| 14.
- block store
- 14.1
-
- 14.1
- borrow
- 14.2.3
- bounded deque
- 3.3
-
- 14.3
- breadth-first traversal
- 6.1.2
- breadth-first-search
- 12.3.1
- celebrity
- see universal sink
-

- 5.1
- chaining
- 5.1
- child
- 6.
- left
- 6.
- right
- 6.
- circular array
- 2.3
- coin toss
- 1.3.4
| 4.4
- collision resolution
- 5.4
- colour
- 9.2
-
- 1.2.4
- comparison tree
- 11.1.4
- comparison-based sorting
- 11.1
- complete binary tree
- 10.1
- complexity
- space
- 1.5
- time
- 1.5
- conflict graph
- 12.
- connected components
- 12.4
- connected graph
- 12.4
- contact list
- 1.
- correctness
- 1.5
-
- 8.2
- counting-sort
- 11.2.1
- credit invariant
- 14.2.4
- credit scheme
- 8.1.1
| 14.2.4
-

- 2.7
- cuckoo hashing
- 5.4
- cycle
- 12.
- cycle detection
- 12.3.2
-

- 10.3
-
- 10.3
- degree
- 12.2
- dependencies
- 1.7
- depth
- 6.
- depth-first-search
- 12.3.2
- deque
- 1.2.1
- bounded
- 3.3
- descendant
- 6.
- dictionary
- 1.2.3
- directed edge
- 12.
- directed graph
- 12.
- disk access model
- 14.3
- divide-and-conquer
- 11.1.1
-
- 3.2
- doubly-linked list
- 3.2
-

- 2.5
- dummy node
- 3.2
- Dyck word
- 1.8
-
- 8.2
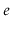 (Euler's constant)
(Euler's constant)
- 1.3.1
- edge
- 12.
- emergency services
- 1.
- Euler's constant
- 1.3.1
- expected cost
- 1.5.0.0.2
- expected running time
- 1.3.4
| 1.5
- expected value
- 1.3.4
- exponential
- 1.3.1
- Ext4
- 14.3
- external memory
- 14.
- external memory hashing
- 14.3
- external memory model
- 14.
- external storage
- 14.
- Eytzinger's method
- 10.1
- factorial
- 1.3.2
- family tree
- 6.3
-

- 2.2
- Fibonacci heap
- 10.3
- FIFO queue
- 1.2.1
- file system
- 1.
- finger
- 4.5
| 7.3
- finger search
- in a skiplist
- 4.5
- in a treap
- 7.3
- fusion tree
- 13.4
- general balanced tree
- 8.2
- git
- Why
- Google
- 1.1.0.0.3
- graph
- 12.
- connected
- 12.4
- strongly-connected
- 12.4
- undirected
- 12.4
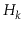 (harmonic number)
(harmonic number)
- 7.1
- hard disk
- 14.
- harmonic number
- 7.1
- hash code
- 5.
| 5.3
- for arrays
- 5.3.2
- for compound objects
- 5.3.2
- for primitive data
- 5.3.1
- for strings
- 5.3.2
- hash function
- perfect
- 5.4
- hash table
- 5.
- cuckoo
- 5.4
- two-level
- 5.4
- hash value
- 5.1
-
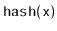
- 5.1
- hashing
- multiplicative
- 5.1.1
| 5.4
- multiply-add
- 5.4
- tabulation
- 7.3
- universal
- 5.4
- hashing with chaining
- 5.1
| 5.4
- heap
- 10.
- binary
- 10.
- binomial
- 10.3
- Fibonacci
- 10.3
- leftist
- 10.3
- pairing
- 10.3
- skew
- 10.3
- heap order
- 10.1
- heap property
- 7.2
- heap-ordered binary tree
- 10.1
- heap-sort
- 11.1.3
- height
- in a tree
- 6.
- of a skiplist
- 4.1
- of a tree
- 6.
- height-balanced
- 9.4
- HFS+
- 14.3
- I/O model
- 14.3
- in-order number
- 6.3
- in-order traversal
- 6.3
- in-place algorithm
- 11.3
- incidence matrix
- 12.4
- indicator random variable
- 1.3.4
- interface
- 1.2
- Java Collections Framework
- 1.8
- leaf
- 6.
- left child
- 6.
- left rotation
- 7.2
- left-leaning property
- 9.2.2
- left-leaning red-black tree
- 9.2.2
- leftist heap
- 10.3
- LIFO queue
- 1.2.1
| see alsostack
- linear probing
- 5.2
-
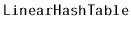
- 5.2
- linearity of expectation
- 1.3.4
- linked list
- 3.
- doubly-
- 3.2
- singly-
- 3.1
- space-efficient
- 3.3
- unrolled
- see also
 �
�
-

- 1.2.2
- logarithm
- 1.3.1
- binary
- 1.3.1
- natural
- 1.3.1
- lower-bound
- 11.1.4
- map
- 1.2.3
- matched string
- 1.8
-
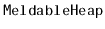
- 10.2
-
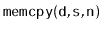
- 2.2
- merge
- 9.1.2
| 14.2.3
- merge-sort
- 3.4
| 11.1.1
- min-wise independence
- 7.3
-
- 3.4
-
- 3.4
-

- 3.4
- modular arithmetic
- 2.3
- multiplicative hashing
- 5.1.1
| 5.4
- multiply-add hashing
- 5.4
-
- 1.6
- natural logarithm
- 1.3.1
- no-red-edge property
- 9.2
- NTFS
- 14.3
- number
- in-order
- 6.3
- post-order
- 6.3
- pre-order
- 6.3
 notation
notation
- 1.3.3
- open addressing
- 5.2
| 5.4
- Open Source
- Why
- ordered tree
- 6.
- pair
- 1.2.3
- pairing heap
- 10.3
- palindrome
- 3.4
- parent
- 6.
- partial rebuilding
- 8.
- path
- 12.
- pedigree family tree
- 6.3
| 10.3
- perfect hash function
- 5.4
- perfect hashing
- 5.4
- permutation
- 1.3.2
- random
- 7.1
- pivot element
- 11.1.2
- planarity testing
- 12.4
- post-order number
- 6.3
- post-order traversal
- 6.3
- potential
- 2.5.1
- potential method
- 2.5.1
| 3.3.5
| 9.3
- pre-order number
- 6.3
- pre-order traversal
- 6.3
- prime field
- 5.3.3
- priority queue
- 1.2.1
| see alsoheap
- probability
- 1.3.4
- queue
- FIFO
- 1.2.1
- LIFO
- 1.2.1
- priority
- 1.2.1
- quicksort
- 11.1.2
- radix-sort
- 11.2.2
- RAM
- 1.4
- random binary search tree
- 7.1
- random permutation
- 7.1
- randomization
- 1.3.4
- randomized algorithm
- 1.3.4
- randomized binary search tree
- 7.3
- randomized data structure
- 1.3.4
-
- 2.7
- reachable vertex
- 12.
- recursive algorithm
- 6.1.1
- red node
- 9.2
- red-black tree
- 9.
| 9.2.2
-
- 9.2.2
- remix
- Why
- right child
- 6.
- right rotation
- 7.2
- rooted tree
- 6.
-
- 2.6
- rotation
- 7.2
- run
- 5.2.1
- running time
- 1.5
- amortized
- 1.5
- expected
- 1.3.4
| 1.5
- worst-case
- 1.5
- scapegoat
- 8.
-
- 8.1
- search path
- in a
- 13.1
- in a binary search tree
- 6.2.1
- in a skiplist
- 4.1
- secondary structure
- 13.3
-

- 3.3
- sentinel node
- 4.1
-
- 8.2
- share
- Why
- simple path/cycle
- 12.
- singly-linked list
- 3.1
- size-balanced
- 6.3
- skew heap
- 10.3
- skiplist
- 4.1
- versus binary search tree
- 4.5
-

- 4.3
-

- 4.2
-
- 3.1
- social network
- 1.
- solid-state drive
- 14.
- sorting algorithm
- comparison-based
- 11.1
- sorting lower-bound
- 11.1.4
- source
- 12.
- space complexity
- 1.5
- spanning forest
- 12.4
- speciation event
- 6.3
- species tree
- 6.3
- split
- 9.1.1
| 14.2.2
- square roots
- 2.6.4
-
- 1.2.4
- stable sorting algorithm
- 11.2.1
- stack
- 1.2.1
-
- 2.2
- Stirling's Approximation
- 1.3.2
- stratified tree
- 13.4
- string
- matched
- 1.8
- strongly-connected graph
- 12.4
- successor search
- 1.2.4
-
- 2.2
- tabulation hashing
- 5.2.3
| 7.3
- target
- 12.
- tiered-vector
- 2.7
- time complexity
- 1.5
- traversal
- breadth-first
- 6.1.2
- in-order
- 6.3
- of a binary tree
- 6.1.2
- post-order
- 6.3
- pre-order
- 6.3
-
- 7.2
-

- 7.3
- tree
- 6.
 -ary
-ary
- 10.3
- binary
- 6.
- ordered
- 6.
- rooted
- 6.
- tree traversal
- 6.1.2
-
- 2.7
- two-level hash table
- 5.4
- underflow
- 14.2.3
- undirected graph
- 12.4
- universal hashing
- 5.4
- universal sink
- 12.4
- unrolled linked list
- see also
 �
�
-
- 1.2.3
- van Emde Boas tree
- 13.4
- vertex
- 12.
- wasted space
- 2.6.2
- web search
- 1.
-

- 8.2
- word
- 1.4
- word-RAM
- 1.4
- worst-case running time
- 1.5
-
- 13.2
- XOR-list
- 3.4
-
- 13.3
opendatastructures.org